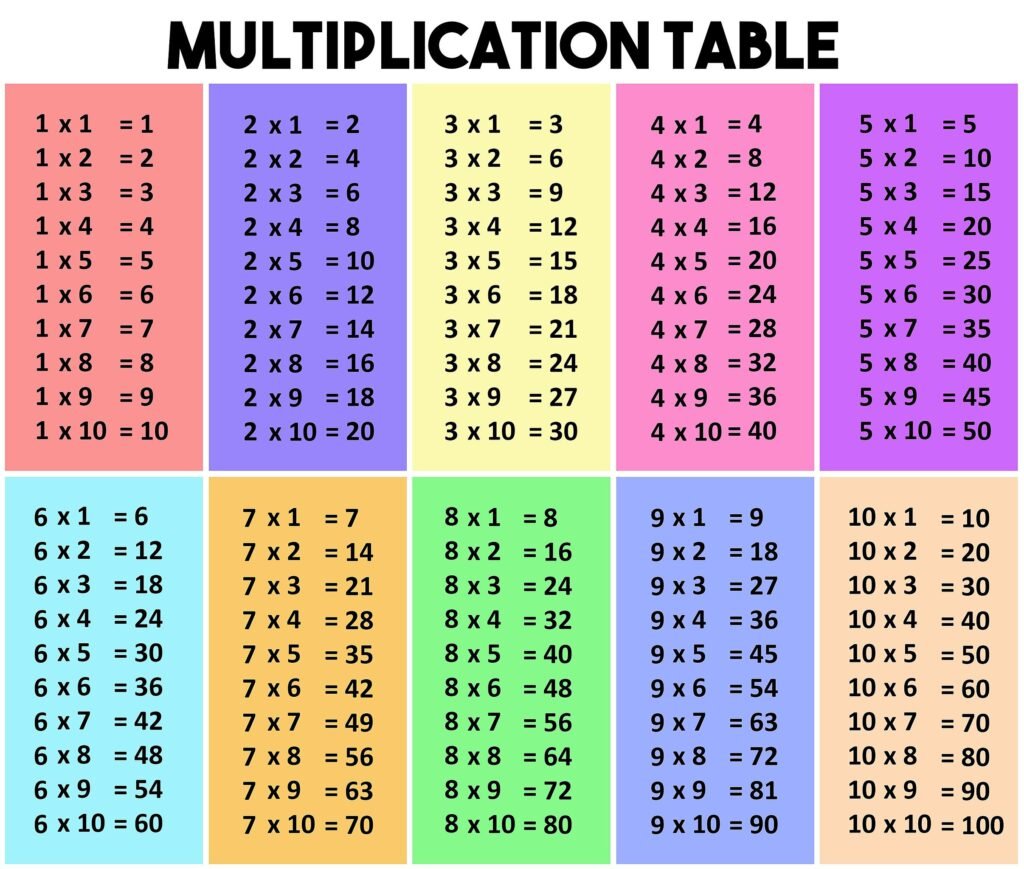
A multiplication table, often referred to as a “times table,” is a structured list that displays the products of pairs of numbers, typically ranging from 1 to 12. This foundational tool is essential in mathematics education, aiding in the understanding and memorization of basic multiplication facts.
Free The Multiplication Table Generator
The Times Tables

A multiplication table, often referred to as a “times table,” is a structured list that displays the products of pairs of numbers, typically ranging from 1 to 12. This foundational tool is essential in mathematics education, aiding in the understanding and memorization of basic multiplication facts.
Historical Background
The concept of the multiplication table dates back thousands of years. The Babylonians, around 4000 years ago, utilized multiplication tables based on a base-60 numeral system. The oldest known decimal (base-10) multiplication table was discovered in China, dating to approximately 305 BC during the Warring States period. This ancient artifact, written on bamboo strips, highlights the long-standing significance of multiplication tables in human history.
What is the easiest way to learn multiplication tables?
Structure of the Multiplication Table
A standard multiplication table is organized in a grid format. The numbers 1 through 12 are listed across the top row and down the first column. The intersection of each row and column provides the product of the corresponding numbers. For example, the cell where row 3 and column 4 intersect contains the number 12, since 3 multiplied by 4 equals 12. This systematic arrangement allows for quick reference and reinforces the commutative property of multiplication, which states that changing the order of factors does not affect the product (i.e., 3 × 4 is the same as 4 × 3).
Learn Multiplication Tables Fast: Tips & Tricks for Kids | He Loves Math
What Is Multiplication?
Multiplication can be defined in the following way: Assume that you have a number a (where a can be any number). If you add a to itself b times, that can be written like this:
| a+a+⋯+a⏟b times |
This can be tiresome in the long run, especially when b becomes large. That’s where multiplication enters the picture. By definition, the sum above can also be written like this:
| a+a+⋯+a⏟b times=b×a |
This means that a added to itself b times is the same as a multiplied by b.
The numbers that are multiplied together are called factors, and the answer is called a product.
Rule
Multiplication
| factor×factor=product |
This might look a little odd—it might not be how you learned about multiplication before. So here’s an example to clarify.
Example 1
You want to add 3 to itself 5 times
This can be written as
| 3+3+3+3+3⏟5 times |
but if you use the definition above, it can also be written as
| 5×3=15 |
Multiplication problems with whole numbers (integers) between 1 and 10 are organized in the times tables. You should learn this table by heart.
Rule
Three Important Rules for Multiplication
- 1.
- a×b=b×a. It does not matter what order the numbers are written in when you multiply—you get the same answer either way!
- 2.
- Anything multiplied by 0 is 0. For example, 5×0×20=0.
- 3.
- If you multiply something by 1, it doesn’t change. For example, 32×1=32.
Understanding the multiplication table is a fundamental skill that supports success in math and beyond. Whether you’re a student trying to master the basics or a parent helping your child understand this key concept, the multiplication table is an essential building block for mathematics. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the importance of learning multiplication tables, practical tips for mastering them, and creative methods to make the learning process enjoyable.
Why Learning the Multiplication Table is Crucial
The multiplication table is at the core of many mathematical concepts. Whether it’s basic arithmetic, fractions, algebra, or even everyday tasks like calculating grocery bills, the multiplication table provides a foundation for these activities. Here are some reasons why learning the multiplication table is so important:
Enhances Problem-Solving Skills: Memorizing multiplication tables helps develop quick recall, which is crucial for solving complex math problems efficiently.
Supports Advanced Learning: Multiplication is the basis for more advanced concepts, including division, fractions, and algebra.
Boosts Confidence: A strong grasp of the multiplication table allows students to approach math with greater confidence, reducing anxiety.
Improves Daily Math Application: Simple multiplication is used in daily life—whether calculating prices, figuring out quantities, or measuring distances. Mastery makes life easier!
Tips for Mastering the Multiplication Table
Mastering the multiplication table doesn’t have to be intimidating. Here are some practical tips to make the process smoother and more effective:
Start Small and Build Confidence
Begin by focusing on smaller numbers, such as the 1s, 2s, 5s, and 10s. These tend to be the easiest and help build a strong foundation. Gradually introduce larger numbers as your understanding and confidence grow.
Use Visual Aids
Visual aids, like multiplication charts, number grids, and flashcards, can be incredibly useful. Charts that illustrate the entire multiplication table allow students to visualize relationships between numbers and recognize patterns.
Practice with Games
Turning learning into a game can make a world of difference. Online multiplication games, board games, and apps provide interactive ways to make practicing tables more engaging. Fun games like “Multiplication Bingo” or “Times Table Hopscotch” can motivate children to practice consistently.
Make It a Routine
Consistency is key. Set aside 10-15 minutes each day for multiplication practice. Repetition helps embed these facts into long-term memory, making it easier for students to recall them quickly.
Sing the Multiplication Tables
Rhymes and songs work wonders for memory. Singing multiplication tables is an effective way to remember them, especially for young learners who respond well to rhythm and repetition.
Creative Ways to Learn the Multiplication Table
Color-Coded Charts
Creating color-coded multiplication charts can help visualize and memorize tables. Use different colors to highlight multiples of numbers and see patterns emerge.
Real-Life Applications
Applying multiplication in real-life scenarios helps solidify understanding. For instance, counting toys in groups, calculating how many cookies will be needed for each guest, or determining the total price of multiple items are all practical ways to bring multiplication into everyday life.
Skip Counting
Skip counting is a great way to understand multiplication. For example, skip counting by 3s (3, 6, 9, 12, etc.) helps students visualize how multiplication tables work.
Use Mnemonics and Tricks
Mnemonics can make remembering multiplication tables easier. For example, with the 9s table, notice that the digits of each product add up to 9 (e.g., 9 x 3 = 27, and 2 + 7 = 9). Tricks like this make it easier to recall multiplication facts.
Multiplication Table Charts: Printable and Handy
Having a handy multiplication table chart is incredibly useful, especially for visual learners. You can easily download and print a multiplication chart for daily use. Keep it on your child’s study desk or the refrigerator for easy access and quick reference.
Download Printable Multiplication Tables: Make sure to have a printable multiplication chart that covers 1 to 12 tables. Having a physical chart allows children to practice without needing a device, minimizing distractions.
Multiplication Table Practice Worksheets
Practice is the ultimate key to mastery. Multiplication worksheets offer students an opportunity to practice in a structured manner. Parents can download worksheets from educational websites or create their own, making sure to focus on different levels—beginner, intermediate, and advanced—to challenge students as they progress.
The Role of Multiplication in Advanced Math
Once students master multiplication, they’re ready to tackle more advanced topics. Algebra, geometry, and even calculus have their roots in multiplication. Mastery of the times tables means students can move forward confidently, equipped with the skills they need for higher learning.
Fractions and Division: Multiplication plays a major role in understanding fractions and division. Knowing the multiplication tables can help students simplify fractions and divide numbers more easily.
Geometry and Measurement: Multiplication is essential for calculating area, perimeter, and volume. It’s a foundational skill for measuring objects and understanding spatial relationships.
Conclusion: The Power of Mastering Multiplication
Learning the multiplication table is one of the most empowering skills a student can acquire. It serves as a gateway to all other mathematical learning and a cornerstone for day-to-day calculations. By using creative techniques, staying consistent, and making learning fun, parents and teachers can help students conquer their multiplication tables with confidence.
Whether you’re a parent looking for the best strategies to support your child or a student wanting to improve your math skills, keep in mind that patience and practice are the keys to success. Mastering multiplication is not just about memorizing numbers—it’s about laying the groundwork for lifelong mathematical confidence.
FAQs
Q1: What is the best way to learn multiplication tables?
The best way to learn multiplication tables is through repetition, using visual aids, practicing with fun games, and applying multiplication in real-life situations.
Q2: How long does it take to learn the multiplication table?
It varies for each student. Some may take a few weeks to master basic tables, while others may need more time. Consistent practice is key.
Q3: Can online games help with multiplication practice?
Absolutely! Many online games are designed to make learning multiplication tables interactive and enjoyable, helping reinforce skills through repetition and fun challenges.
30 detailed FAQs about multiplication tables that are designed to be informative and engaging:
What is a multiplication table?
A multiplication table is a chart or grid showing the results of multiplying two numbers together. It’s commonly arranged with numbers 1-10 or 1-12 on both axes, showing products in a matrix format. It helps learners quickly find answers to basic multiplication problems.Why is the multiplication table important?
Learning multiplication tables strengthens foundational math skills, improves mental arithmetic, and helps solve more complex math problems, including fractions, algebra, and geometry, efficiently.At what age should children start learning multiplication tables?
Children generally start learning multiplication tables around age 7 or 8, or in the 2nd or 3rd grade, depending on their readiness and the school curriculum.How do you read a multiplication table?
To read a multiplication table, find the first number on the horizontal axis, then the second number on the vertical axis. The point where these meet is the product (result) of the two numbers.What is the easiest way to learn multiplication tables?
Learning through repetition, games, flashcards, or using multiplication songs or rhymes can make memorizing tables easier. Breaking it down, like focusing on one table a week, also helps.Are there tricks for memorizing multiplication tables?
Yes, some tricks include using patterns, such as knowing that any number multiplied by 10 ends in zero or that multiplying by 5 always results in a number ending in 0 or 5.Why do multiplication tables usually go up to 12?
Multiplication tables often go up to 12 because it covers all numbers typically encountered in basic math. Additionally, many measurement systems and time units (like inches or hours) are based on multiples of 12.How can multiplication tables help in everyday life?
Multiplication tables assist in quick calculations for budgeting, shopping (like unit prices), cooking (scaling recipes), and understanding time management without needing a calculator.Can multiplication tables help with division?
Yes, multiplication tables can help with division by using the inverse relationship between multiplication and division. For example, knowing 6×4=246 \times 4 = 246×4=24 helps with 24÷6=424 \div 6 = 424÷6=4.What is the ‘commutative property’ in multiplication tables?
The commutative property states that the order of multiplication doesn’t affect the product. For instance, 3×43 \times 43×4 is the same as 4×34 \times 34×3.How does understanding multiplication tables improve math confidence?
Memorizing tables gives quick recall of answers, reduces the need for long calculations, and allows students to focus on problem-solving without the distraction of basic math operations.Is it necessary to memorize all multiplication tables?
While it’s helpful, focusing on tables up to 12 can be sufficient for most basic math tasks. As students advance, understanding patterns can replace rote memorization.How can I make multiplication tables fun for my child?
Use games, online apps, or hands-on activities like multiplication bingo or flashcards. Incorporating fun challenges and rewards can also make learning engaging.Are multiplication tables still relevant in the age of calculators?
Absolutely. Multiplication tables build mental math skills, which aid in faster problem-solving, logic building, and everyday tasks where a calculator may not be available.What are some patterns in the multiplication table?
Patterns include the “even-odd” rule (even numbers multiply to make even products), the “9’s trick” (sum of digits in multiples of 9 equals 9), and repeating end digits in multiples of 5 and 10.How do multiplication tables relate to arrays?
Arrays visually represent multiplication tables by arranging objects in rows and columns. For example, 3×43 \times 43×4 can be shown as three rows with four objects in each row.What’s the best way to practice multiplication tables daily?
Regularly practice using flashcards, apps, or by quizzing oneself. Setting a small daily goal, like focusing on one multiplication set, helps build fluency over time.How does understanding multiplication tables help with fractions?
Multiplication tables help simplify fractions by making it easier to find common denominators or to multiply fractions and mixed numbers efficiently.What is skip-counting, and how does it help in multiplication tables?
Skip-counting is counting by numbers like 2, 3, 4, etc., instead of by 1. It’s a technique for building multiplication skills, as it teaches children to count in groups.Why are the 1 and 10 tables the easiest to learn?
The 1 and 10 tables follow simple patterns: any number multiplied by 1 is itself, and numbers multiplied by 10 have an added zero at the end, making them easy to remember.How can visual aids help with multiplication tables?
Visual aids like charts, colored grids, or number lines can help learners see multiplication patterns and reinforce memory by associating colors or visual patterns with numbers.How are multiplication tables used in higher math?
Multiplication is foundational in algebra, calculus, and geometry. Knowing tables aids in simplifying equations, working with exponents, and solving higher-level problems.What’s the difference between multiplication tables and times tables?
Multiplication tables and times tables are essentially the same; both show the products of multiplying two numbers. “Times tables” is a more informal term often used in elementary education.What are some multiplication table games?
Games like “Times Table Bingo,” “Roll and Multiply,” online multiplication quizzes, or flashcard races can make learning multiplication tables engaging and competitive.How can apps help with learning multiplication tables?
Apps often provide interactive and repetitive learning through games, quizzes, and challenges, making practice enjoyable and reinforcing memory.What role does multiplication play in real-world careers?
Multiplication is essential in fields like finance, engineering, architecture, cooking, and sales, where accurate and quick calculations are critical.How can I test my multiplication table knowledge?
Take timed quizzes, play multiplication games, or work on mental math challenges where you solve random multiplication problems without a calculator.Why are multiplication tables often taught before division?
Multiplication tables form the foundation for understanding division, as division is the inverse of multiplication. Learning tables first makes division easier to grasp.Can multiplication tables help with estimating?
Yes, knowing multiplication tables helps quickly estimate quantities, prices, or measurements by rounding to the nearest factor or calculating in multiples.What are some common challenges in learning multiplication tables?
Challenges include memorizing large sets of numbers and understanding patterns. Breaking down tables, using visual aids, and practicing regularly can help overcome these difficulties.What is a multiplication table?
A multiplication table is a mathematical chart used to define the product of two numbers. Typically, it lists numbers 1 through 12 along the top row and the leftmost column. The intersection of a row and column provides the product of the corresponding numbers. For example, the intersection of row 3 and column 4 displays 12, since 3 multiplied by 4 equals 12.
Why is learning the multiplication table important?
Mastering the multiplication table is fundamental in mathematics education. It aids in the quick recall of multiplication facts, which is crucial for more advanced mathematical concepts such as division, fractions, and algebra. A solid grasp of multiplication facilitates problem-solving and analytical thinking.
At what age should children start learning the multiplication table?
Children typically begin learning multiplication tables between the ages of 7 and 9, corresponding to second or third grade in many educational systems. However, the appropriate age can vary depending on individual readiness and the specific curriculum.
What are effective methods for teaching multiplication tables?
Several strategies can enhance the learning of multiplication tables:
Repetition and Practice: Regular practice helps reinforce memory.
Patterns Recognition: Identifying patterns within the table (e.g., any number times 10 ends in zero) can simplify learning.
Use of Mnemonics: Rhymes or songs can make memorization more engaging.
Interactive Tools: Utilizing educational apps and games can make learning interactive and fun.
How can I help my child if they struggle with multiplication tables?
If a child is struggling, consider the following approaches:
Break Down the Table: Focus on one number at a time to avoid overwhelming them.
Use Visual Aids: Incorporate charts or flashcards to provide visual reinforcement.
Relate to Real-Life Situations: Apply multiplication to everyday scenarios to demonstrate its practicality.
Positive Reinforcement: Celebrate successes to build confidence and encourage progress.
Are there patterns in the multiplication table that can aid learning?
Yes, several patterns can assist learners:
Commutative Property: The order of factors doesn’t affect the product (e.g., 3 × 4 is the same as 4 × 3).
Multiplying by 1: Any number multiplied by 1 remains unchanged.
Multiplying by 10: Any number multiplied by 10 ends in zero.
Even and Odd Patterns: Even numbers multiplied result in even products; an even number multiplied by an odd number also results in an even product.
How does the multiplication table relate to division?
Understanding multiplication tables directly supports division skills. Since division is the inverse of multiplication, knowing that 3 × 4 = 12 helps in understanding that 12 ÷ 3 = 4. This relationship reinforces both operations and enhances numerical fluency.
Can technology assist in learning multiplication tables?
Absolutely. Numerous educational apps and online games are designed to make learning multiplication tables engaging and interactive. These tools often adapt to a child’s learning pace, providing customized practice and feedback.
What is the historical origin of the multiplication table?
The concept of the multiplication table dates back thousands of years. The Babylonians used early forms of multiplication tables around 4000 years ago. The oldest known decimal multiplication table was discovered in China, dating to approximately 305 BC during the Warring States period. This highlights the long-standing significance of multiplication in human history.
Are there cultural differences in multiplication tables?
While the basic concept of multiplication tables is universal, the format and range can vary. For instance, some countries emphasize tables up to 10 × 10, while others extend to 12 × 12 or higher. Additionally, teaching methods and mnemonics can differ based on cultural and educational practices.
What is the difference between a multiplication table and a multiplication chart?
A multiplication table, also known as a times table, is a structured list that displays the products of pairs of numbers, typically ranging from 1 to 12. A multiplication chart, on the other hand, is a visual representation of these products in a grid format, where the rows and columns intersect to show the result of multiplying two numbers. Both tools serve the same purpose of aiding in the learning and memorization of multiplication facts.
How can I use a multiplication chart effectively?
To use a multiplication chart effectively, follow these steps:
Identify the numbers to be multiplied: Locate one number on the top row and the other on the leftmost column.
Find the intersection: Trace down from the top row number and across from the leftmost column number to find the cell where they intersect; this cell contains the product.
Practice regularly: Use the chart to test yourself by covering parts of it and trying to recall the products, gradually reducing reliance on the chart.
Are there any tricks to learning specific multiplication tables?
Yes, certain multiplication tables have patterns or tricks that can aid in learning:
6 Times Table: When multiplying 6 by an even number, the product ends in the same digit as the even number being multiplied. For example, 6 × 4 = 24; both 4 and 24 end in 4.
9 Times Table: The sum of the digits in the products of 9 always equals 9. For instance, 9 × 3 = 27 (2 + 7 = 9).
11 Times Table: For numbers 1 through 9, multiplying by 11 results in a doubling of the original number (e.g., 11 × 3 = 33).
What are the properties of multiplication?
Multiplication has several key properties:
Commutative Property: Changing the order of factors does not change the product (e.g., 4 × 5 = 5 × 4).
Associative Property: The way factors are grouped does not affect the product (e.g., (2 × 3) × 4 = 2 × (3 × 4)).
Distributive Property: Multiplying a number by a sum is the same as multiplying each addend individually and then adding the products (e.g., 2 × (3 + 4) = (2 × 3) + (2 × 4)).
Identity Property: Any number multiplied by 1 remains unchanged (e.g., 7 × 1 = 7).
Zero Property: Any number multiplied by 0 equals 0 (e.g., 5 × 0 = 0).
How does multiplication relate to addition?
Multiplication is essentially repeated addition. For example, 4 × 3 means adding 4 three times: 4 + 4 + 4 = 12. This relationship helps in understanding the concept of multiplication and in performing calculations mentally.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when learning multiplication tables?
Common mistakes include:
Relying solely on rote memorization without understanding: It’s important to understand the concept of multiplication as repeated addition.
Ignoring patterns: Not recognizing patterns within the tables can make learning more difficult.
Lack of regular practice: Infrequent practice can lead to forgetting the tables; consistent review is key.
How can adults improve their multiplication skills?
Adults can improve their multiplication skills by:
Using multiplication apps or online tools: These can provide interactive and engaging ways to practice.
Applying multiplication in daily life: Practice calculating prices, measurements, or quantities mentally.
Teaching others: Explaining concepts to someone else can reinforce one’s own understanding.
What role does the multiplication table play in advanced mathematics?
A solid understanding of multiplication tables is foundational for advanced mathematical concepts, including algebra, calculus, and beyond. It aids in simplifying expressions, solving equations, and understanding functions.
Can multiplication tables be used for numbers beyond 12?
Yes, multiplication tables can be extended beyond 12. While traditional tables often cover 1 through 12, creating or using extended tables can help in learning products of larger numbers, which is useful in various mathematical applications.
Are there cultural differences in teaching multiplication tables?
Yes, different cultures may have varying approaches to teaching multiplication tables. For instance, some countries emphasize memorization up to 10 × 10, while others may extend to 12 × 12 or higher. Additionally, methods and tools used for teaching, such as songs, rhymes, or visual aids, can vary across cultures.
What is the difference between a multiplication table and a multiplication chart?
A multiplication table, also known as a times table, is a structured list that displays the products of pairs of numbers, typically ranging from 1 to 12. A multiplication chart, on the other hand, is a visual representation of these products in a grid format, where the rows and columns intersect to show the result of multiplying two numbers. Both tools serve the same purpose of aiding in the learning and memorization of multiplication facts.
How can I use a multiplication chart effectively?
To use a multiplication chart effectively, follow these steps:
Identify the numbers to be multiplied: Locate one number on the top row and the other on the leftmost column.
Find the intersection: Trace down from the top row number and across from the leftmost column number to find the cell where they intersect; this cell contains the product.
Practice regularly: Use the chart to test yourself by covering parts of it and trying to recall the products, gradually reducing reliance on the chart.
Are there any tricks to learning specific multiplication tables?
Yes, certain multiplication tables have patterns or tricks that can aid in learning:
6 Times Table: When multiplying 6 by an even number, the product ends in the same digit as the even number being multiplied. For example, 6 × 4 = 24; both 4 and 24 end in 4.
9 Times Table: The sum of the digits in the products of 9 always equals 9. For instance, 9 × 3 = 27 (2 + 7 = 9).
11 Times Table: For numbers 1 through 9, multiplying by 11 results in a doubling of the original number (e.g., 11 × 3 = 33).
What are the properties of multiplication?
Multiplication has several key properties:
Commutative Property: Changing the order of factors does not change the product (e.g., 4 × 5 = 5 × 4).
Associative Property: The way factors are grouped does not affect the product (e.g., (2 × 3) × 4 = 2 × (3 × 4)).
Distributive Property: Multiplying a number by a sum is the same as multiplying each addend individually and then adding the products (e.g., 2 × (3 + 4) = (2 × 3) + (2 × 4)).
Identity Property: Any number multiplied by 1 remains unchanged (e.g., 7 × 1 = 7).
Zero Property: Any number multiplied by 0 equals 0 (e.g., 5 × 0 = 0).
How does multiplication relate to addition?
Multiplication is essentially repeated addition. For example, 4 × 3 means adding 4 three times: 4 + 4 + 4 = 12. This relationship helps in understanding the concept of multiplication and in performing calculations mentally.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when learning multiplication tables?
Common mistakes include:
Relying solely on rote memorization without understanding: It’s important to understand the concept of multiplication as repeated addition.
Ignoring patterns: Not recognizing patterns within the tables can make learning more difficult.
Lack of regular practice: Infrequent practice can lead to forgetting the tables; consistent review is key.
How can adults improve their multiplication skills?
Adults can improve their multiplication skills by:
Using multiplication apps or online tools: These can provide interactive and engaging ways to practice.
Applying multiplication in daily life: Practice calculating prices, measurements, or quantities mentally.
Teaching others: Explaining concepts to someone else can reinforce one’s own understanding.
What role does the multiplication table play in advanced mathematics?
A solid understanding of multiplication tables is foundational for advanced mathematical concepts, including algebra, calculus, and beyond. It aids in simplifying expressions, solving equations, and understanding functions.
Can multiplication tables be used for numbers beyond 12?
Yes, multiplication tables can be extended beyond 12. While traditional tables often cover 1 through 12, creating or using extended tables can help in learning products of larger numbers, which is useful in various mathematical applications.
Are there cultural differences in teaching multiplication tables?
Yes, different cultures may have varying approaches to teaching multiplication tables. For instance, some countries emphasize memorization up to 10 × 10, while others may extend to 12 × 12 or higher. Additionally, methods and tools used for teaching, such as songs, rhymes, or visual aids, can vary across cultures.
Multiplication Grid Table
Useful for learning times tables and also for helping with other maths tasks.
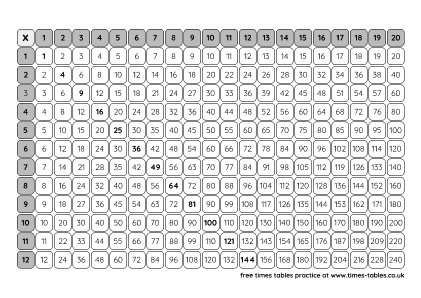
A4 Black & White
(Landscape, pdf)
Free Printable Times Tables Sheets
Tables from 1 though to 12 individually laid out.
(Landscape, pdf)

(Landscape, pdf)

(Landscape, pdf)

Frequently Asked Questions: Learning Multiplication & More
How to learn multiplication tables?
Learning multiplication tables effectively involves several strategies:
- Start Small: Begin with easier tables like 0, 1, 2, 5, and 10.
- Visual Aids: Use a multiplication chart to see patterns.
- Regular Practice: Short, consistent practice sessions are key. Use flashcards, apps, or online games.
- Break it Down: Focus on one table at a time until mastered.
- Look for Patterns: For example, the 9s table digits add up to 9 (9x2=18, 1+8=9).
- Relate to Addition: Understand that multiplication is repeated addition (e.g., 3x4 = 4+4+4).
- Say them Aloud: Reciting tables helps with memorization.
How to memorize multiplication tables fast?
To memorize multiplication tables quickly:
- Focus on Understanding, Not Just Rote: Knowing why 7x8=56 is better than just chanting it.
- Use Mnemonics: Create rhymes or stories for tricky facts (e.g., "5, 6, 7, 8! Fifty-six is seven times eight!").
- Chunking: Learn facts in small groups.
- Timed Drills: Challenge yourself with timed quizzes once you have some basics down.
- Use Music/Songs: Many songs exist to help learn tables.
- Identify and Target Weak Spots: Focus extra effort on the facts you find hardest.
- The Commutative Property: Remember that 3x7 is the same as 7x3. This halves the number of facts to learn!
How to teach multiplication tables in a fun way?
Make learning engaging:
- Games: Use board games, card games (Multiplication War), or online interactive games.
- Songs and Chants: Turn tables into catchy tunes.
- Storytelling: Create stories around numbers and their products.
- Hands-on Activities: Use manipulatives like blocks or counters to represent multiplication.
- Real-World Connections: Show how multiplication is used in everyday life (e.g., shopping, cooking).
- Positive Reinforcement: Offer praise and small rewards for effort and progress.
- Peer Learning: Have students quiz each other or work in groups.
What is a multiplication table?
A multiplication table (or times table) is a list of multiples of a particular number. Typically, it shows the results of multiplying that number by a sequence of other numbers, usually from 1 to 10 or 1 to 12.
For example, the multiplication table for 3 would include: 3x1=3, 3x2=6, 3x3=9, and so on.
A full multiplication grid or chart displays all these tables together, usually in a square format, making it easy to find the product of any two numbers within the range.
How to learn multiplication tables in one day?
While truly mastering all tables in a single day is ambitious for most, you can make significant progress with intense focus:
- Clear your schedule: Dedicate several hours without distractions.
- Start with the easiest: Quickly master 0, 1, 10, 11 (up to 9x11 is easy pattern). This builds confidence.
- Use patterns for 2s, 5s: 2s are just doubling, 5s end in 0 or 5.
- Tackle the 9s trick: The sum of digits is 9, and the tens digit is one less than the multiplier. (e.g., 9x7: tens digit is 6, 6+3=9, so 63).
- Focus on squares: 3x3, 4x4, etc., are often easier to remember.
- Break down remaining facts: For 7x8, if you know 7x7=49, add another 7 to get 56.
- Constant review: Use flashcards and self-testing throughout the day.
- Realistic expectations: Aim for strong familiarity rather than flawless, instant recall for all facts in just one day. True mastery takes time and repetition.
What are multiplication facts?
Multiplication facts are the basic multiplication equations that are typically memorized. They usually involve multiplying two single-digit numbers (e.g., 7 x 8 = 56) or a single-digit number by numbers up to 10 or 12.
Knowing these facts by heart is crucial for performing more complex mathematical calculations quickly and accurately.
What times what equals 32?
The pairs of whole numbers that multiply to 32 are:
- 1 x 32 = 32
- 2 x 16 = 32
- 4 x 8 = 32
And their reverses (32x1, 16x2, 8x4).
What is x + 12?
x + 12 is an algebraic expression. It represents a value that is 12 more than the value of 'x'.
Without knowing the value of 'x', we cannot determine a specific numerical answer. The expression itself is the answer if 'x' is undefined.
For example:
- If x = 5, then x + 12 = 5 + 12 = 17.
- If x = -2, then x + 12 = -2 + 12 = 10.
What is 6+6+6+6x0?
To solve this, we need to follow the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS: Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction).
- Multiplication first: 6 x 0 = 0
- Then Addition: 6 + 6 + 6 + 0
- 6 + 6 = 12
- 12 + 6 = 18
- 18 + 0 = 18
So, 6+6+6+6x0 = 18.
What is 2 2/3 + 1 1/2?
To add mixed numbers, you can convert them to improper fractions or add the whole parts and fractional parts separately.
Method 1: Improper Fractions
- 2 2/3 = (2*3 + 2)/3 = 8/3
- 1 1/2 = (1*2 + 1)/2 = 3/2
- Find a common denominator for 3 and 2, which is 6.
- 8/3 = (8*2)/(3*2) = 16/6
- 3/2 = (3*3)/(2*3) = 9/6
- Add the fractions: 16/6 + 9/6 = 25/6
- Convert back to a mixed number: 25 ÷ 6 = 4 with a remainder of 1. So, 4 1/6.
Method 2: Add Whole and Fractional Parts
- Add whole parts: 2 + 1 = 3
- Add fractional parts: 2/3 + 1/2
- Common denominator for 3 and 2 is 6:
- 2/3 = 4/6
- 1/2 = 3/6
- Add fractions: 4/6 + 3/6 = 7/6
- Convert 7/6 to a mixed number: 1 1/6
- Add this to the sum of whole parts: 3 + 1 1/6 = 4 1/6.
How to create a table in Excel with multiple columns?
Creating a table in Excel is straightforward:
- Enter your data: Type your column headers in the first row of your desired table location (e.g., A1 for "Name", B1 for "Age", C1 for "City").
- Input data rows: Fill in the data under each header.
- Select your data: Click and drag to highlight all the cells containing your headers and data.
- Format as Table:
- Go to the "Home" tab, and in the "Styles" group, click "Format as Table". Choose a style you like.
- Alternatively, go to the "Insert" tab and click "Table".
- Confirm range and headers: In the "Create Table" dialog box, Excel usually auto-detects your data range. Ensure the "My table has headers" box is checked if you included them. Click "OK".
Your data is now an official Excel table, which provides benefits like easy sorting, filtering, and structured references.
How to create a pivot table from multiple sheets?
Creating a PivotTable from multiple sheets in Excel typically involves consolidating your data first or using Power Query (Get & Transform Data).
Method 1: Using Power Query (Recommended for modern Excel versions)
- Ensure each sheet has data in a consistent tabular format with headers.
- For each sheet: Select the data range, go to the "Data" tab, and click "From Table/Range" to load it into Power Query.
- In the Power Query Editor, you can clean/transform data if needed. Once done for one table, choose "Close & Load To..." and select "Only Create Connection". Repeat for all sheets.
- Go to "Data" > "Get Data" > "Combine Queries" > "Append".
- In the Append dialog, choose your tables (two, or three or more) and click "OK". This creates a new query with all data combined.
- Click "Close & Load To..." and choose "PivotTable Report" on a new or existing worksheet.
Method 2: Using the old "PivotTable and PivotChart Wizard" (for older Excel versions or specific needs)
- Press
Alt+D, thenPto open the wizard. - Select "Multiple consolidation ranges" and click "Next".
- Choose "Create a single page field for me" or "I will create the page fields" and click "Next".
- Add the range from each sheet one by one using the "Add" button.
- Specify where to put the PivotTable and click "Finish".
Power Query is generally more flexible and powerful for this task.
How to join multiple tables in SQL?
In SQL, you join multiple tables using JOIN clauses in your SELECT statement. The type of JOIN determines how rows are combined:
- INNER JOIN: Returns rows when there is a match in both tables based on the join condition.
SELECT columns FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.common_column = table2.common_column; - LEFT JOIN (or LEFT OUTER JOIN): Returns all rows from the left table (table1), and the matched rows from the right table (table2). If there's no match, NULLs are returned for columns from the right table.
SELECT columns FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.common_column = table2.common_column; - RIGHT JOIN (or RIGHT OUTER JOIN): Returns all rows from the right table (table2), and the matched rows from the left table (table1). If there's no match, NULLs are returned for columns from the left table.
SELECT columns FROM table1 RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.common_column = table2.common_column; - FULL JOIN (or FULL OUTER JOIN): Returns all rows when there is a match in either the left or right table. If there's no match in one of the tables, NULLs are returned for its columns.
SELECT columns FROM table1 FULL JOIN table2 ON table1.common_column = table2.common_column;
You can join more than two tables by adding more JOIN clauses:
SELECT ... FROM table1 JOIN table2 ON ... JOIN table3 ON ...;
Can a table have multiple primary keys?
No, a table in a relational database can have only one primary key.
However, a primary key can be composite, meaning it can be made up of multiple columns. In such a case, the combination of values in these columns must be unique for each row and none of them can be NULL.
For example, in a table linking students to courses they've enrolled in, the primary key might be (StudentID, CourseID). Individually, StudentID might not be unique (a student can take multiple courses), and CourseID might not be unique (a course can have multiple students), but the combination of a specific student and a specific course is unique for each enrollment record.
How to make a time table (for study/daily routine)?
Creating an effective time table involves several steps:
- List Your Tasks/Subjects: Write down everything you need to schedule (e.g., study subjects, work, breaks, meals, exercise, leisure).
- Prioritize: Determine which tasks are most important or require more time/focus.
- Allocate Time Slots: Divide your day into manageable time blocks (e.g., hourly, or based on typical activity durations).
- Assign Tasks to Slots: Fill in your time table. Be realistic about how much you can achieve in each slot.
- Schedule difficult tasks for when you are most alert.
- Alternate between different types of tasks to maintain focus.
- Include Breaks: Regular short breaks are crucial to avoid burnout and maintain productivity (e.g., 5-10 minutes every hour). Also schedule longer breaks for meals.
- Be Flexible: Your first time table might not be perfect. Allow for adjustments and unexpected events. Build in some buffer time.
- Review and Revise: At the end of each day or week, review your time table. What worked? What didn't? Adjust for the next period.
- Tools: You can use a paper planner, a spreadsheet (like Excel or Google Sheets), a digital calendar app, or dedicated time table apps.
Consistency is key. Stick to your time table as much as possible to build good habits.